Therapeutic Management of Fibromyalgia Syndrome (FMS)
Fibromyalgia is a complex syndrome characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue despite rest or sleep, stiffness, memory impairment and mood disturbances. Exact etiology for the condition is unknown. However, the pathogenesis of FMS is theorized to be a cluster of causes including biochemical, immunological, neurohormonal and physiological abnormalities. These abnormalities lead to a central nervous system disorder causing central sensitization and heightened pain perception (hyperalgesia, allodynia, referred pain etc). FMS may also develop following stressful events like traumatic accidents, surgery, infections or significant psychological stress. While there is no obvious cure for fibromyalgia treatment, physical therapy may help alleviate the symptoms of pain, spasm or stiffness.
Clinical presentation
Often people come to see a physical therapist with complain of generalized muscle pain (myalgia, aching or burning type) and persistent fatigue (mental and physical).
According to the Copenhagen Fibromyalgia Syndrome definition, two criteria for the diagnosis of FMS are;
- Widespread pain (four-quadrant; both above and below the waistline) lasting at least 3 months
- The presence of at least 11 positive tender points out of a total 18.
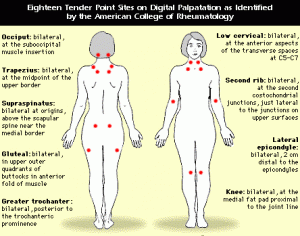
Other complaints include;
- Sleep disturbances with generalized morning stiffness
- Muscle spasm
- Cold intolerance
- Irritable bladder or bowel
- Restless legs
- Headaches
- Visual problems
- Cognitive impairments; impaired memory, decreased attention and concentration, mood disorders
- Anxiety and depression
- Unusual pain, numbness, and tingling sensations
- GI problems (constipation, diarrhea)
- FMS is not a joint disorder. There is no inflammatory or degeneration of joints, muscles or connective tissues.
Fibromyalgia Treatment
Physical Therapy is one of the best options for Fibromyalgia treatment to alleviate the symptoms and reduce the impact on patient’s daily life. Physical therapy aims to reduce pain, improve muscle flexibility, and improve joint range of motion and education.
Aerobic and resistance training
Patients typically demonstrate exercise intolerance. However, total bed rest or sleep is not advised but the levels of activities are reduced. Without activities, problems of spasm, stiffness, tender points get more severe. Physical therapy for fibromyalgia treatment mainly focuses on preventing deconditioning. Aerobic and resistance exercises are carefully designed as per the individual assessment and needs. Ottawa panel evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (2008) highly recommended the inclusion of light aerobic exercise and resistance training in fibromyalgia treatment.
NEXT: Exercise Guideline


