Decorticate and Decerebrate Rigidity. Abnormal Posturing.

The presence of abnormal posturing is a severe medical emergency and thus immediate medical attention is warranted. Abnormal posturing is an indication of severe brain injury which can result in coma. There is an involuntary severe flexion or extension of the arms and legs, and sometimes trunk and neck as well. This abnormal posturing is mainly due to the debilitation of one set of muscles due to injury while the opposing set is not. An external stimulus such as pain then causes only one set of working muscles to contract to increase a severe muscle tone. Therefore, abnormal posturing is the result of severe rigidity. There are mainly three types abnormal posturing; Decorticate rigidity, Decerebrate rigidity, and Opisthotonus.
Rigidity
Rigidity is a hypertonic state of muscles independent of the velocity of movement and characterized by continuous resistance to movement. It is a form of sustained efferent muscular hyperactivity due to continuous supraspinal drive to the alpha motor neuron.
Muscle tone is typically graded on a 0 to 4+ scale for the medical record:
0 No response (flaccidity)
1+ Decreased response (hypotonia)
2+ Normal response
3+ Exaggerated response (mild to moderate hypertonia)
4+ Sustained response (severe hypertonia)
Decorticate Rigidity:
Decorticat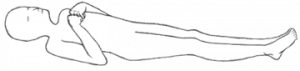 e rigidity or decorticate posturing is a type of abnormal posturing also called as flexor posturing, colloquially or mummy baby. It is characterized by the 4+ sustained contraction response and posturing of the upper limbs in flexion and the lower limbs in extension. The shoulders are adducted tightly to the sides while the elbows, wrists, and fingers are flexed or clenched into fists. The legs are extended or straightened, internally rotated or feet turned inward and plantarflexed. Medically, this form of rigidity is the indicative of a corticospinal tract lesion at the level of the diencephalon (above the superior colliculus).
e rigidity or decorticate posturing is a type of abnormal posturing also called as flexor posturing, colloquially or mummy baby. It is characterized by the 4+ sustained contraction response and posturing of the upper limbs in flexion and the lower limbs in extension. The shoulders are adducted tightly to the sides while the elbows, wrists, and fingers are flexed or clenched into fists. The legs are extended or straightened, internally rotated or feet turned inward and plantarflexed. Medically, this form of rigidity is the indicative of a corticospinal tract lesion at the level of the diencephalon (above the superior colliculus).
Decerebrate Rigidity
Decerebrate posturing or rigidity is an involuntary extension posture of both upper and lower extremities with head and trunk arched back. The arms are extended and adducted by the sides, elbows extended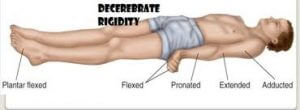 , forearm pronated, and wrist and fingers flexed. While legs are fully extended and stiffened with feet internal rotation and plantarflexed. The patient is usually severely rigid, with the teeth clenched. This stiffness is usually both sides but can be unilateral, can be in the arms only or can be intermittent. Medically, decerebrate rigidity is an indicative of a corticospinal tract lesion at the level of brainstem between the superior colliculus and vestibular nucleus.
, forearm pronated, and wrist and fingers flexed. While legs are fully extended and stiffened with feet internal rotation and plantarflexed. The patient is usually severely rigid, with the teeth clenched. This stiffness is usually both sides but can be unilateral, can be in the arms only or can be intermittent. Medically, decerebrate rigidity is an indicative of a corticospinal tract lesion at the level of brainstem between the superior colliculus and vestibular nucleus.
Opisthotonus
This form of an abnormal posture is the severely rigid hyperextended posture with a strong and sustained contraction of the extensor muscles of the neck and trunk. Sometimes, proximal limbs extensor muscles are also involved.
Common causes of abnormal posturing or severe rigidity
- Traumatic brain injury
- Increased intracranial pressure
- Stroke
- Brain tumors
- Intracranial hemorrhage
- Encephalopathy
- Head injuries
- Diffuse cerebral hypoxia
- Brain abscesses
- Creutzreldt-Jakob disease

Hello. Thanks a lot! Really enjoyed reading this page.
I wanted to thank you for this amazing read!! I undoubtedly loving
every little bit of it I have you bookmarked
to have a look at new material you post.
Hi there! This post could not be written any better! Reading through this post
reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept talking about this.
I will forward this post to him. Fairly sure he will have a
great read. Thank you for sharing!
Wonderful article thank you for sharing.
Woah! I’m really digging the template/theme of this website. It’s simple, yet effective. A lot of times it’s difficult to get that “perfect balance” between usability and visual appeal. I must say you’ve done a amazing job with this. Additionally, the blog loads super fast for me on Firefox. Exceptional Blog!
Great information. Blessed me I reach on your site by accident,
I bookmarked it.
Thankyou Lorna. Look forward to more feedbacks
Limb posturing can also be caused by untreated phenylketonuria and various mitochondrial issues