Sports Rehabilitation. The role of the biomechanist and physiotherapist as a team for athletes’ wellbeing and performance.
The Biomechanist Approach
Biomechanics is the sports science field that applies the laws of mechanics and physics to human performance, in order to gain a greater understanding of performance in athletic events through modeling, simulation, and measurement.
The Biomechanical Approach to Injury
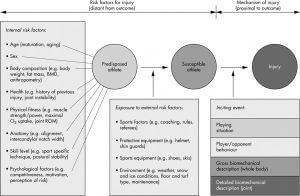
Bahar et al 2005
A comprehensive model for injury causation.
Role of the biomechanist as a team member of a sports rehabilitation team.
A Bio-mechanist work together with a sports rehabilitation team including physiotherapist, sports Dr, the strength and conditioning team and the coach.
The biomechanist focuses on movement accuracy at a very high level and identify when patterns are incorrect before they become high risk and can either effectively communicate this with the rehab team, or treat/prescribe/advice to improve outcomes either in the gym or out in training.
Coaches and biomechanist work together to identify a fault in the athletes’ technique that is creating pain or is inhibiting progression to higher level performance.
Specific screening methods for athletes used by the biomechanist.
Uses multiple screening techniques to create a holistic screen for the athlete:
a. complete history of the athlete including sporting history, injury history (inclusive reports and notes where possible), professional history, personal history (simple example is female athletes who have had children)
b. Dynamic Screening I: using various software to look at the movement patterns, force generation, loading forces on joints or muscles, ground reaction forces etc of the athlete running or sporting under normal loading
c. Static Screening: isolated muscle balance testing, where possible adapted to be sport-specific
d. Dynamic Screening II: functional movement screening including squat, single leg squat, rotational patterns etc.
This combined screening gives a complete picture as to what it is the root cause of the movement issues.
Unique features as a biomechanist
A very detailed knowledge of movement patterns within the specific sports.
High-level understanding of correcting biomechanical alignments and thereby correcting faulty movement patterns. Thus, prevent sports injuries.
Assesses the injuries as a possible complex, dynamic pattern or higher/lower kinetic chain involvement rather than focussing only on the injury site.
Exercise programming from very low-level exercise to correct faulty movement patterns to the most effective highest level exercise to ensure effective movements that exceed the requirements of their particular sports.
A very high-level understanding of gait, running, agility, and postural training.
Work as a team member of a sports rehabilitation team
There is a strong ethical guideline on what the biomechanist can and can’t assess.
Usually, the athletes’ physiotherapist or sports doctor will advise on their findings and recommendations for exercise prescription.
The biomechanist has extensive knowledge on exercise prescription especially to ensure most effective movement patterns, posture or biomechanical alignment, muscles and joints balance. Thus, considering the guidelines from the physiotherapist on faulty movement patterns, the biomechanist can quickly progress the athlete from low-level rehab-based prescription to movement-specific performance and maintenance.
The performance gains come via an extrapolation to movement with improved activation patterns.
United team approach
A strong united team approach is the key to ensuring athlete’s wellbeing and performance.
Especially, the coaches must work together with sports rehabilitation and exercise training team. This ensures athlete’s wellbeing rather than controlling them and pushing them too much beyond.
The coach must overall direct the athlete, but he/she must have a strong team around them to advise and discuss the athlete’s wellbeing and performance.
Regular team communication, well-defined understanding of roles and scope of practice, and an understanding of the athletes’ psychology on coping and performance is the key to success in sports rehabilitation, performance and injury prevention.
Research
- Finch (2005) highlights the importance of translating all the current sporting injury research into good clinical practice for injury prevention. This has been named the Translating Research into Injury Prevention Practice framework, or TRIPP program. Thus opening the doors to biomechanists becoming integral parts of the sports injury prevention team through utilization of their expertise on body mechanics and forces.
- Biomechanist has studied the importance of maintaining knee control during the jump phase of netball. Hewett et al (2005) concluded that knee motion and knee loading during a landing task are predictors of anterior cruciate ligament injury risk in female athletes. Therefore using a biomechanist knowledge of the mechanics of the lower limbs a pre-rehab or rehabilitation program can be implemented to prevent future injury.
- Biomechanists analytical approach has lead to important strategies that have lead to rule changes, alteration of training techniques and improvement in equipment and footwear throughout the sporting world. (Taunton et al 1988)
- Bahar (2005) developed a biomechanical approach to injury (similar to that found in the latest edition of Bruknar and Khan’s, Clinical Sports medicine). The model can be used to study the interaction between different factors causing injury and address the potential for prevention.
Conclusion
- Biomechanists are an integral part of the multidisciplinary team when considering the elite to top end age group athlete
- Biomechanists are a highly useful adjunct to physiotherapy when considering the mechanics of the whole kinetic chain in the everyday athlete
- They do have ethical guidelines/limitations, they can not diagnose but they can suggest and implement treatment protocols.
- Utilization of a biomechanists skills has been clinically proven to improve performance in athletes and also can prevent injury.
Reference



hello!,I love your writing very much! percentage we be in contact more about your article on AOL? I need an expert in this area to solve my problem. May be that’s you! Taking a look forward to see you.
I’ve been surfing online more than 3 hours today, yet I never found any interesting article like yours. It’s pretty worth enough for me.